Basic Concept Videos
Intermediate Microeconomic Theory I
- These are the basic videos in Intermediate Microeconomic Theory I . This is taught at Delhi University, Semester III
- If you are from Delhi University, Economics H, then this is the complete syllabus which you have to follow. Readings which are followed are
- Hal Varian, Intermediate Microeconomics
- Nicholson and Snyder, Fundamentals of Microeconomics
- In Delhi University, in semester III, they teach
- Consumer Theory
- Production and Cost Theory
- Perfect Competition (Market Structures) [ This topic I have kept in my videos in Microeconomics II, so if you are preparing for semester III, then you will have to follow Perfect Competition videos from there]
- If you are from Non Economics Background or from Economics background but some other texts are used in your university, you can learn from these videos, concepts still remain same, whichever text is used
- These videos are arranged in the order in which they should be done. Pick up your pen and register, and start writing them out. Nothing is difficult, anything could be learned, put your effort in this and start making notes.
- If these videos are in anyway helpful to you, if they have helped you in any exam, whether Semester, or any other public exam, please drop us a mail
-

Cobb Douglas Utility function : Demand curve /Normal Good/Substitutes or Complements/Elasticity |2|
-

Perfect Complements Utility |Demand curve /Normal Good/Elasticity/Engel Curve/ Income Offer Curve|3|
-

Demand function for Perfect Substitutes and One Simple Application | 4 |
-

Quasilinear Preferences, Income Offer curve and Engel Curve. | 5 |
-

Indifference Curves : Tangency Condition and Optimal Choice | 6 |
-

Corner Solutions in Indifference Curve (Part 1) :U = max{x,y} | 7 |
-

Corner Solutions in Indifference Curve (Part 2) : U = x^2 + y^2 |Concave Preferences| | 8 |
-

Corner Solutions|Indifference Curve :(Part 3)|lexicographic Preferences| Economic Bads| Neutral |9|
-

Monotonicity of Preferences | Why Indifference Curves are Downward Sloping| | 10 |
-

Averages are preferred to extremes | Well Behaved Preferences| |11|
-

Diminishing MRS | Numerical Examples | Test of Diminishing MRS | |MRS as the ratio of MU | |12|
-

Monotonic Transformation of a Utility Function | Meaning | Definition | Example | 13 |
-

Homethetic Preferences (Part 1) | Meaning | Definition | Simple Proof | 14 |
-

Homethetic Preferences (Part 2)|All Homogenous are Homothetic|Not all Homothetic are Homogenous|15|
-

Homothetic functions(Part 3)| Income expansion Path | Elasticity |Constant MRS along a ray |16|
-

Weak Axiom of Revealed Preference | Meaning | Example | 17 |
-

Weak Axiom of Revealed Preference (Part 2) | Violation of WARP | 18 |
-

Weak Axiom of Revealed Preference (Part 3) | Violation of WARP Numerical Example | 19 |
-

Revealed Preference (Part 4) | Strong Axiom of Revealed Preference | Meaning | Numerical | 20 |
-

Substitution Effect and Income Effect |Meaning | Diagram | Simple Numerical Example | 21 |
-

Sign of Substitution Effect | Revealed Preference Argument | 22 |
-

Hicksian Substitution Effect| Non Positive Nature of Hicksian Substitution Effect | 23 |
-

Slutsky Identity | Slutsky Equation | Normal goods | Inferior Goods | Giffen Goods| 24 |
-

Substitution effect & Income Effect | Perfect Complements | Perfect Substitutes | Quasilinear | 25 |
-

Intertemporal Choice | Budget Constraint | Present Value Form and Future Value Form | 26 |
-

Intertemporal Choice | When Lender remains a lender | When Borrower remains a borrower| 27 |
-

Intertemporal Choice and Slutsky Equation | 28 |
-

Index numbers | Revealed Preference | Lasperyers and Paasche Quantity Index | 29 |
-

Index numbers | Revealed Preference | Lasperyers and Paasche Price Index | 30 |
-

Intertemporal Choice | Kinked Budget Constraint | Numerical Example | 31 |
-
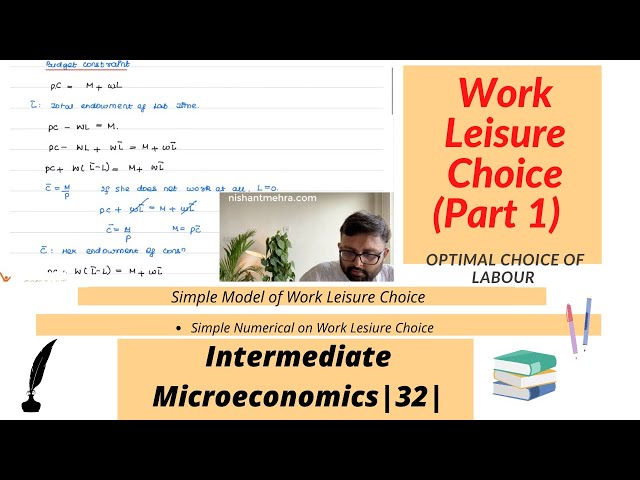
Work Leisure Choice (Part 1) | Budget Constraint | Labour Supply | Numerical Example | 32 |
-

Work Leisure Choice Part 1 | Budget Constraint | Labour Supply | Numerical Example | 32 | HINDI |
-

Backward Bending Supply Curve of Labour | Work Leisure Choice (Part II) | | 33 |
-

Overtime Wages and Pure Substitution Effect | Work Leisure Choice (Part 3) | 34 |
-

Choice Under Uncertainty | Part 1 | Meaning of Expected Value and Expected Utility | 35 |
-

Choice Under Uncertainty | Part 2 | Risk Averse Individual and Fair Bet | 36 |
-
![[Choice Under Uncertainty] | Part 3 | Risk Aversion | Risk Premium | Certainty Equivalence | 37 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ZNr1HZyOTbk/sddefault.jpg)
[Choice Under Uncertainty] | Part 3 | Risk Aversion | Risk Premium | Certainty Equivalence | 37 |
-
![[Choice Under Uncertainty] Part 4 | Demand for Insurance | Actuarially Fair Insurance Premium | 38 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ab1g3A8-ijk/sddefault.jpg)
[Choice Under Uncertainty] Part 4 | Demand for Insurance | Actuarially Fair Insurance Premium | 38 |
-

Production Theory Basics | Part 1 | Production Function | Isoquant | MRTS | 39 |
-
![[Production Theory Basics] | Part 2 | Relation between Diminishing MU and Diminishing MRTS | 40 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/aEVOUB-MWh4/sddefault.jpg)
[Production Theory Basics] | Part 2 | Relation between Diminishing MU and Diminishing MRTS | 40 |
-
![[Production Theory Basics] | Part 3 | Returns to Scale | CRS | IRS | DRS |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/W2SBCUA6ZOI/sddefault.jpg)
[Production Theory Basics] | Part 3 | Returns to Scale | CRS | IRS | DRS |
-
![[Production Theory Basics] Elasticity of Substitution | High & Low elasticity of substitution | 42 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/XQBLV2VMj3E/sddefault.jpg)
[Production Theory Basics] Elasticity of Substitution | High & Low elasticity of substitution | 42 |
-

Examples of Elasticity of Substitution | Cobb Douglas | Perfect Complement | Perfect Substitutes|43|
-
![[Production Theory Basics] [Part 6] Technical Progress using the production function concept | 44 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/YlceDtQdVOE/sddefault.jpg)
[Production Theory Basics] [Part 6] Technical Progress using the production function concept | 44 |
-
![[Production Theory Basics] Part 7 | Numerical Examples from Production Theory | 45 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/pBf7rL5Mw5M/sddefault.jpg)
[Production Theory Basics] Part 7 | Numerical Examples from Production Theory | 45 |
-
![[Cost Theory Basics] Meaning of Cost Minimisation | Tangency between Isocost Line and Isoquant |46|](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/TeCqvDD8BaI/sddefault.jpg)
[Cost Theory Basics] Meaning of Cost Minimisation | Tangency between Isocost Line and Isoquant |46|
-

Derivation of Cost function from production function | Cobb Douglas | Perfect Complements |47|
-
![[Cost Theory Basics] [Part 3 ] |Conditional Input Demand Function Responses |Comparative Statics|48|](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/8InEUCykPLs/sddefault.jpg)
[Cost Theory Basics] [Part 3 ] |Conditional Input Demand Function Responses |Comparative Statics|48|
-
![[Cost Theory Basics] [Part 4] Short run and Long Run Costs | Cobb Douglas Production function | 49 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/LvDQatlWXeQ/sddefault.jpg)
[Cost Theory Basics] [Part 4] Short run and Long Run Costs | Cobb Douglas Production function | 49 |
-
![[Cost Theory Basics] [Part 5] Relation between AC and MC | Interpretation | Numerical Example | 50 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/XbT2Dyjfc9U/sddefault.jpg)
[Cost Theory Basics] [Part 5] Relation between AC and MC | Interpretation | Numerical Example | 50 |
Intermediate Microeconomic Theory II
- These are the basic videos in Intermediate Microeconomic Theory II . This is taught at Delhi University, Economics H, Semester IV. This is a work in progress. I am still in the process of making these videos
- If you are from Delhi University, Economics H, then this is the complete syllabus which you have to follow. Readings which are followed are
- Hal Varian, Intermediate Microeconomics
- Nicholson and Snyder, Fundamentals of Microeconomics
- In Delhi University, in semester IV, they teach
- General Equilbrium Analysis
- Welfare Economics
- Market Structures
- Perfect Competition
- Imperfect Competion
- Monopoly
- Oligopoly
- Monopolistic Competition
- Game Theory (Basic Non Cooperative Games)
- Asymmetric Information : Moral Hazard and Adverse Selection
- Public Goods and Externalities
- If you are from Non Economics Background or from Economics background but some other texts are used in your university, you can learn from these videos, concepts still remain same, whichever text is used
- These videos are arranged in the order in which they should be done. Pick up your pen and register, and start writing them out. Nothing is difficult, anything could be learned, put your effort in this and start making notes.
- If these videos are in anyway helpful to you, if they have helped you in any exam, whether Semester, or any other public exam, please drop us a mail
-

Basics of Edgeworth Box Diagram | Net Buyer | Net Seller | Feasible Allocation | 1 |
-
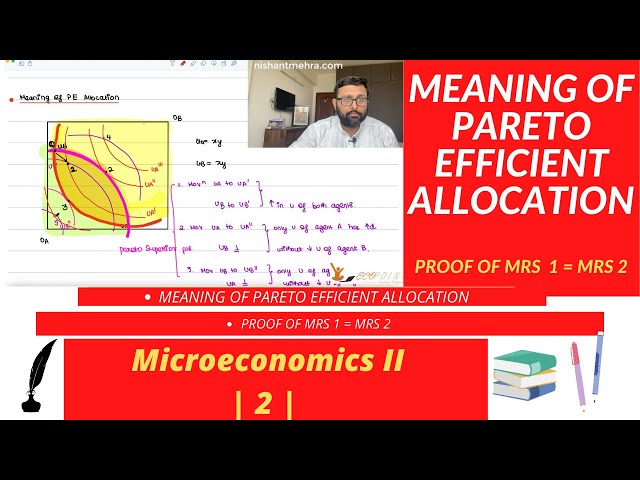
Meaning of Pareto Efficient Allocation |2|
-

Examples of Pareto Efficiency | Numerical | Cobb Douglas- Cobb Douglas | Cobb Douglas - Min | 3 |
-

Competitive Equilibrium Condition MRS 1 = MRS 2 = Price Ratio | 4 |
-
![[Microeconomics II] Walras Law | Value of Aggregate excess demand vector is zero at all prices | 5 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/7CYWNuSgmQE/sddefault.jpg)
[Microeconomics II] Walras Law | Value of Aggregate excess demand vector is zero at all prices | 5 |
-
![[Microeconomics II] Numerical | Competitive Equilbrium Price and Allocation | 7 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/uGLtVQEc5Zo/sddefault.jpg)
[Microeconomics II] Numerical | Competitive Equilbrium Price and Allocation | 7 |
-
![[Microeconomics II ] Walras Law | Another Proof | 6 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/8aEoYbjS1vA/sddefault.jpg)
[Microeconomics II ] Walras Law | Another Proof | 6 |
-
![[Microeconomics II] First Welfare Theorem | Proof | All Market Equilibrium are Pareto efficient |8|](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/euemMxqd8PQ/sddefault.jpg)
[Microeconomics II] First Welfare Theorem | Proof | All Market Equilibrium are Pareto efficient |8|
-
![[Microeconomics II] First Welfare Theorem | Simple Monopoly Case | 9 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/MVgCdw19wI0/sddefault.jpg)
[Microeconomics II] First Welfare Theorem | Simple Monopoly Case | 9 |
-
![[Microeconomics II] First Welfare Theorem | Part 3 | Perfectly Discriminating Monopolist | 10 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/PHSNvTvf5KE/sddefault.jpg)
[Microeconomics II] First Welfare Theorem | Part 3 | Perfectly Discriminating Monopolist | 10 |
-
![[Microeconomics II] Second Welfare Theorem | Convex Preferences | Non Convex Preferences | 11 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/FaalTkc0L40/sddefault.jpg)
[Microeconomics II] Second Welfare Theorem | Convex Preferences | Non Convex Preferences | 11 |
-
![[Microeconomics II] Welfare Economics | Aggregation of Preferences | Majority Voting Method | 12 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/I476IpVemRU/sddefault.jpg)
[Microeconomics II] Welfare Economics | Aggregation of Preferences | Majority Voting Method | 12 |
-
![[Microeconomics II] Welfare Economics | Rank Order Voting | Condorcet Paradox | Borda Count | 13 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/sTmH1Kpn3nI/sddefault.jpg)
[Microeconomics II] Welfare Economics | Rank Order Voting | Condorcet Paradox | Borda Count | 13 |
-
![[Microeconomics II] Welfare Economics | Arrow Impossibility Theorem | Meaning | Part 1 | 14 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/8DLYFgIPom4/sddefault.jpg)
[Microeconomics II] Welfare Economics | Arrow Impossibility Theorem | Meaning | Part 1 | 14 |
-
![[Microeconomics II] Welfare Economics | Arrow Impossibility Theorem | Part 2 | 15 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/KyNVlkD7kF0/sddefault.jpg)
[Microeconomics II] Welfare Economics | Arrow Impossibility Theorem | Part 2 | 15 |
-
![[Microeconomics II] | Types of Social Welfare Functions | Benthamite | Rawlasian | Nietzsian |16 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/FRkzDLid6uI/sddefault.jpg)
[Microeconomics II] | Types of Social Welfare Functions | Benthamite | Rawlasian | Nietzsian |16 |
-
![[Microeconomics II]Maximization of Welfare | Utility Possibility Frontier | Iso Welfare curves |17|](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/TjqAYex11NM/sddefault.jpg)
[Microeconomics II]Maximization of Welfare | Utility Possibility Frontier | Iso Welfare curves |17|
-
![[Microeconomics II] | Any Pareto Optimal Allocation must be Welfare Maximizing for some SWF | 18 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/xPESVAgS2iw/sddefault.jpg)
[Microeconomics II] | Any Pareto Optimal Allocation must be Welfare Maximizing for some SWF | 18 |
-
![[Game Theory Introduction] | Dominant Strategy Equilibrium | Meaning of Nash Equilibrium | 19 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/_QCLbdpYU_0/sddefault.jpg)
[Game Theory Introduction] | Dominant Strategy Equilibrium | Meaning of Nash Equilibrium | 19 |
-
![[Basics Of Game Theory] | Is Nash Equilibrium Unique and Pareto optimal | Will it always exist |20|](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/fKLE6hQi_MQ/sddefault.jpg)
[Basics Of Game Theory] | Is Nash Equilibrium Unique and Pareto optimal | Will it always exist |20|
-
![[Game Theory Basics] Mixed Strategy Nash Equilibrium Example | Best Response Functions | 21|](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Uwjo2U1fEJw/sddefault.jpg)
[Game Theory Basics] Mixed Strategy Nash Equilibrium Example | Best Response Functions | 21|
-
![[Game Theory Basics] Sequential Form Games | Battle of Sexes | Non Credible Threat | 22 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Cc4o_i4J_Vk/sddefault.jpg)
[Game Theory Basics] Sequential Form Games | Battle of Sexes | Non Credible Threat | 22 |
-
![[Game Theory Basics] Subgame Perfect Nash Equilibrium Example | Wrting Strategies of Players | 23 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/MgULBFqTVYg/sddefault.jpg)
[Game Theory Basics] Subgame Perfect Nash Equilibrium Example | Wrting Strategies of Players | 23 |
-

Perfect Competition | Part 1| Features | Demand Curve of a Firm in Perfect Competition | 24 |
-

Market Structures Basics | Part 2 | Perfect Competition | Profit Maximizing Condition P= MC | 25 |
-

Market Structures Basics | Part 3 | P= MC is not a sufficient condition | Shut Down Point | 26 |
-

Market Structures | Part 4 | Perfect Competition |Producer Surplus = Profits plus Fixed Costs | 27 |
-

Market Structures | Part 5 | Perfect Competition| Numericals| Supply Function | Producer Surplus|28|
-

Market Structures Basics | Part 6 | Marginal Revenue and Elasticity | Perfect Competition | 29 |
-

Market Structures | Part 7| Profit Maximization | Example | Cobb Douglas Production Function | 30 |
-

Market Structures | Part 8 | Short Run Profit Maximization |Value of Marginal Product = wage| 31 |
-

Market Structures | Part 9 | Isoprofit Lines and VMP=W condition | Comparative Statics | 32 |
-

Market Structures | Monopoly | Part 1 | Meaning of a Monopoly and Barriers to Entry | 33 |
-

Monopoly | Part 2| Monopoly Profit Max | Monopolist will never operate at inelastic portion | 34 |
-

Market Structures Basics | Monopoly | Part 3 | Meaning and Derivation of Lerner's Index | 35 |
-

Market Structures | Monopoly | Part 4 |Deadweight loss of Monopoly | Inefficiency of a Monopoly |36|
-

Market Structures | Monopoly | Part 5 | Monopoly and Product Quality | 37|
-

Monopoly | Part 6 | First Degree (Perfect) Price Discrimination | No Deadweight loss | 38 |
-

Monopoly | Part 7 | Third Degree Price Discrimination | Meaning | Mathematical Condition | 39|
-

Monopoly | Part 8 | Calculating Third Degree Price Discrimination | Uniform Pricing |40 |
-

Monopoly | Part 9 | Natural Monopoly | Meaning | Features | Diagram | 41 |
-
![[Market Structures] Oligopoly | Part 1 | Bertrand Equilibrium | Proof of Bertrand Nash P=MC | 42 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/U7sd2syRlLA/sddefault.jpg)
[Market Structures] Oligopoly | Part 1 | Bertrand Equilibrium | Proof of Bertrand Nash P=MC | 42 |
-
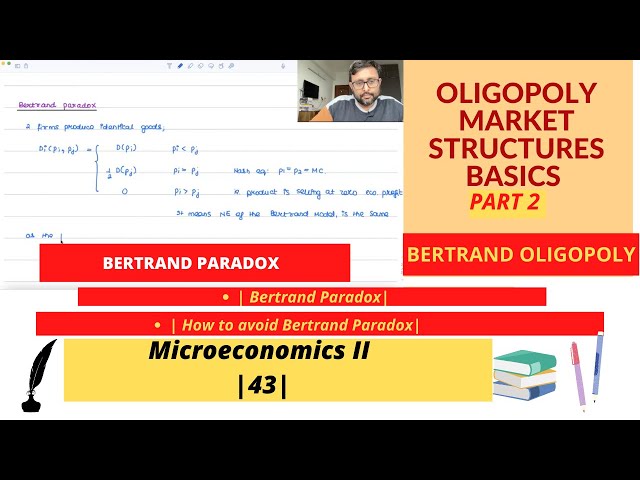
Oligopoly Market Structures | Part 2 | Bertrand Paradox | Avoid Bertrand Paradox | 43 |
-

Oligopoly |Part 3 | Market Structures | Cournot Equilibrium | Numerical | Efficiency | 44 |
-
![[Market Structures] Oligopoly | Part 4 | Bertrand vs Cournot Comparison. |45 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/YGizpyniO3k/sddefault.jpg)
[Market Structures] Oligopoly | Part 4 | Bertrand vs Cournot Comparison. |45 |
-
![[Oligopoly Market Structures] | Part 5 | Capacity Constraints under Bertrand Competition | 46 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/1e7P3gtn4rU/sddefault.jpg)
[Oligopoly Market Structures] | Part 5 | Capacity Constraints under Bertrand Competition | 46 |
-
![[Oligopoly Market Structures] | Part 6 | Bertrand Competition with Differentiated Products | 46 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/JbTWz_6rDc4/sddefault.jpg)
[Oligopoly Market Structures] | Part 6 | Bertrand Competition with Differentiated Products | 46 |
-
![[Oligopoly Market Structures] | Part 7 | Tacit Collusion | Finitely Repeated Game | 48 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/yxOv1Bp-cmw/sddefault.jpg)
[Oligopoly Market Structures] | Part 7 | Tacit Collusion | Finitely Repeated Game | 48 |
-
 | Tacit Collusion | Infinitely Repeated Game | 49 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ErT4KANRvaE/sddefault.jpg)
[Oligopoly Market Structures ]( Part 8) | Tacit Collusion | Infinitely Repeated Game | 49 |
-

Asymmetric Information | Examples | Meaning | Part 1 | 50 |
ECONOMETRICS
- This is taught at Semester IV , Economics H, Delhi University
- The text which is followed is ” Essentials of Econometrics” by Gujarati
- I am in the process of making these videos
- If you want to learn Econometrics, these videos can serve as a starting point, but again the expectation is that you will be reading the text side by side and making notes; then only you can gain full benefit out of them
- If these videos are in anyway helpful to you, if they have helped you in any exam, whether Semester, or any other public exam, please drop us a mail
-
![[Econometrics] Population Regression Line | Meaning | Stochastic PRF | Non Stochastic PRF | 1 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/N80_bawA5rQ/sddefault.jpg)
[Econometrics] Population Regression Line | Meaning | Stochastic PRF | Non Stochastic PRF | 1 |
-
![[Econometrics] Sample Regression Function | Nature of Stochastic Error Term | 2 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/2JqvVpCfn6M/sddefault.jpg)
[Econometrics] Sample Regression Function | Nature of Stochastic Error Term | 2 |
-
![[Econometrics] Linear in Parameters | Method of OLS | Estimation Intercept and Slope terms | 3 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/kV_pcrDdsHw/sddefault.jpg)
[Econometrics] Linear in Parameters | Method of OLS | Estimation Intercept and Slope terms | 3 |
-
![[Econometrics] Properties of Regression Line | 4 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/pKPnoTGJ-Mk/sddefault.jpg)
[Econometrics] Properties of Regression Line | 4 |
-

[Econometrics| Assumptions of CLRM | Classical Linear Regression Model | 5 |
-
![[Econometrics] Unbiasedness of Slope Estimator | Simple Proof | 6 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/bxunEoP3FcY/sddefault.jpg)
[Econometrics] Unbiasedness of Slope Estimator | Simple Proof | 6 |
-
![[Econometrics] Variance of Regression Coefficients | Slope estimator | beta two hat | 7 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/gUoG2QugQYM/sddefault.jpg)
[Econometrics] Variance of Regression Coefficients | Slope estimator | beta two hat | 7 |
-
![[Econometrics] Gauss Markov Theorem | PART 1 | Unbiasedness | Variance of beta 2 hat | | 8 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/vtTbDkHQZlY/sddefault.jpg)
[Econometrics] Gauss Markov Theorem | PART 1 | Unbiasedness | Variance of beta 2 hat | | 8 |
-
![[Econometrics] Gauss Markov Theorem | Part 2 | Proof | Minimum Variance | | 9 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/f3HN6yFvOsI/sddefault.jpg)
[Econometrics] Gauss Markov Theorem | Part 2 | Proof | Minimum Variance | | 9 |
-
![[Econometrics] Coefficient of Determination r2 | TSS = ESS + RSS | 10 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/aJJuH6Ay5oo/sddefault.jpg)
[Econometrics] Coefficient of Determination r2 | TSS = ESS + RSS | 10 |
-
![[Econometrics] Regression through Origin | Without Intercept Model | 11 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/jQiNL-HZdZ0/sddefault.jpg)
[Econometrics] Regression through Origin | Without Intercept Model | 11 |
-
![[Econometrics] Scaling and Units of Measurement | 12 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/BCw9JbwoV8M/sddefault.jpg)
[Econometrics] Scaling and Units of Measurement | 12 |
-

Introductory Econometrics | Functional Forms | Log Lin Model | Meaning and Interpretation |13 |
-

Introductory Econometrics | Functional Forms | Log Lin Model How to calculate growth rates | 14 |
-

Introductory Econometrics | Functional Forms | Lin Log Model | Meaning and Interpretation | 15 |
-

Introductory Econometrics and Statistics | Random Variable | Bernoulli Random Variable | 16 |
-

Econometrics & Statistics | Discrete Random Variable & Probability distribution function | 17 |
-
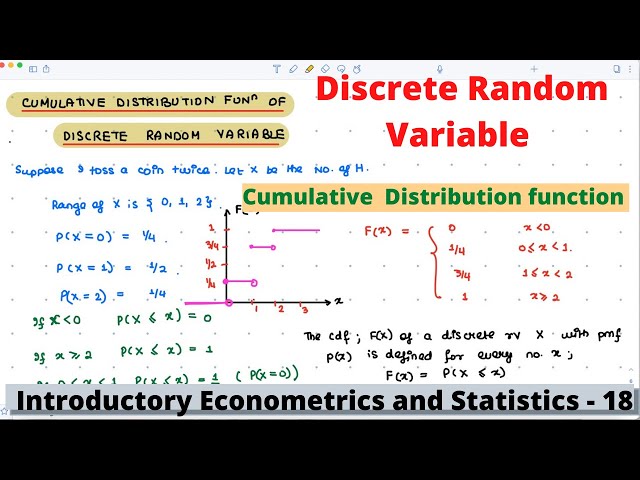
Econometrics and Statistics | Cumulative Distribution Function | Example | 18 |
-

Econometrics and Statistics | Continuous Random Variable | Probability Distribution Function |19|
-

Econometrics and Statistics | Mathematical Expectation of a discrete random variable | Examples|20|
-
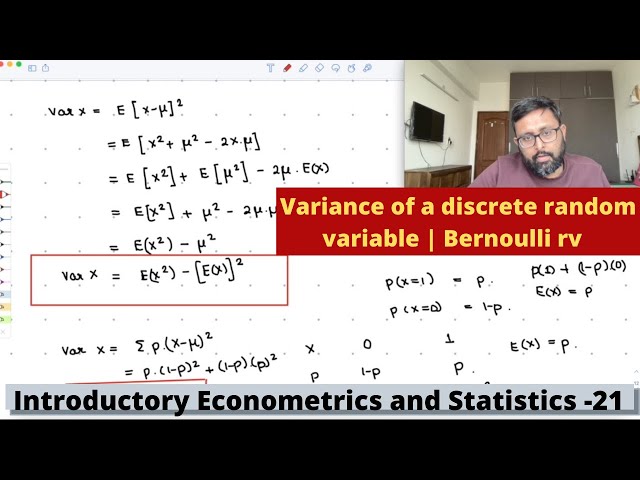
Econometrics and Statistics | Variance of a discrete random variable | Bernoulli rv | 21 |
-

Econometrics and Statistics | Questions on Variance of discrete rv | Change of origin and scale |22|
-
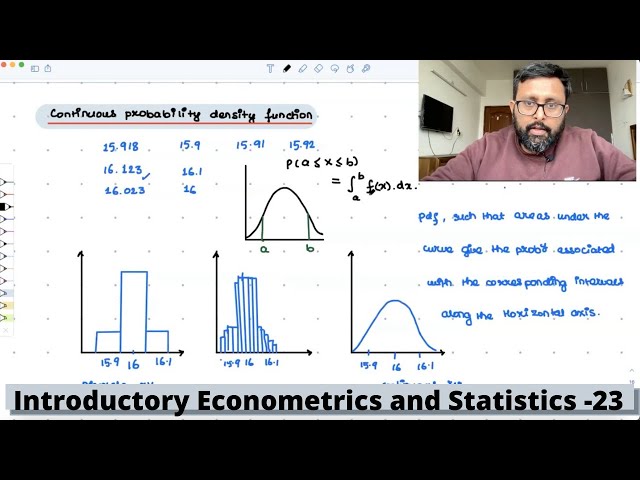
Introductory Econometrics and Statistics | Continuous Probability Density functions | Examples | 23|
-

Cumulative Density function of a Continuous Random Variable | Examples | 24 |
-

Econometrics and Statistics | Expectation of a continuous random variable | Examples | 25 |
-
Deleted video
-

Joint Probability Distribution | Discrete random variable | Definition | Example | 26 |
-

Joint Probability Distribution & Joint Cumulative Distribution Function | Discrete rv | 27 |
-

Joint Probability Density Function of a continuous random variable | Definition | Example | 28 |
-

Marginal Distribution Function | Marginal Density Function | 29 |
-

Introductory Econometrics and Statistics | Conditional Distribution | Definition | Example | 30 |
-

Introductory Econometrics and Statistics | Moments about Origin and Arbitrary Point | 31 |
-

Moments about Mean | Central Moments | Meaning , Definition and Basic Properties | 32 |
-
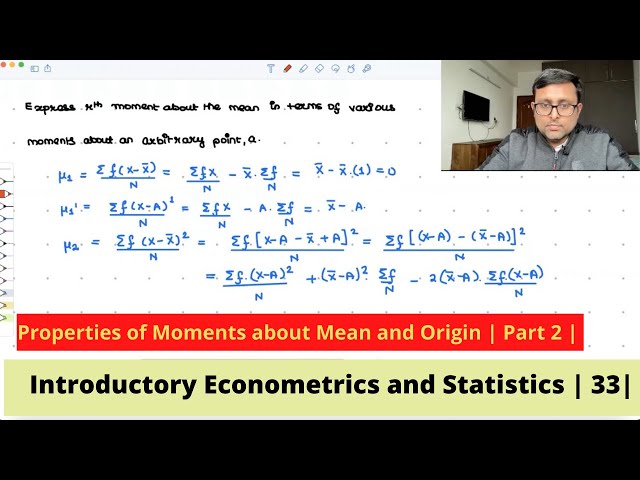
Introductory Econometrics and Statistics | Properties of Moments about mean and origin | Part 2 |
-

Introductory Econometrics and Statistics | Numerical on Moments about mean and origin | 34 |
-
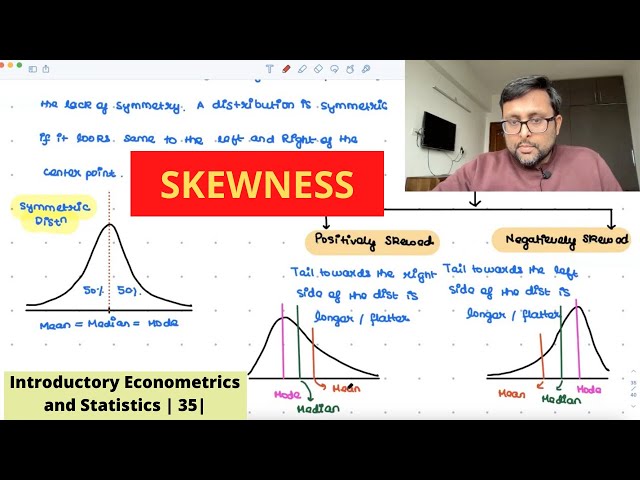
Skewness | Meaning and Types | Formula | Positively Skewed | Negatively Skewed | 35 |
-

Measures of Skewness | Karl Pearson's measure of Skewness | Bowley's measure of Skewness | 36 |
-

Kurtosis | Meaning | Types | Mesokurtic | Leptokurtic | Platykurtic | 37 |
-

Binomial Distribution | Mean and Variance | Meaning | Difference from Bernoulli distribution | 38 |
-
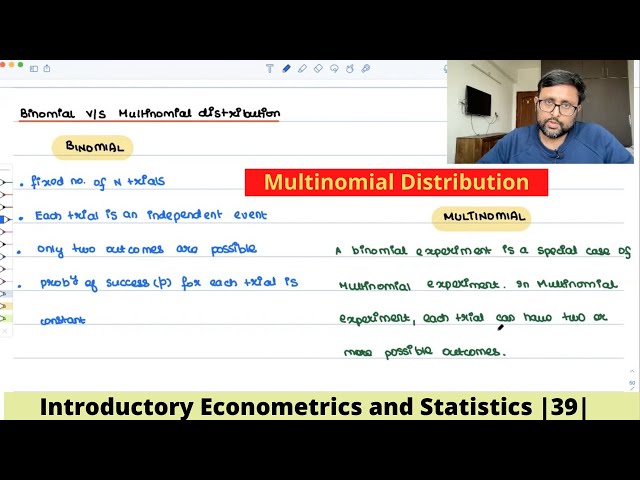
Multinomial Distribution | Meaning | Example | 39 |
-

Negative Binomial Distribution | Meaning | Example | 40 |
-
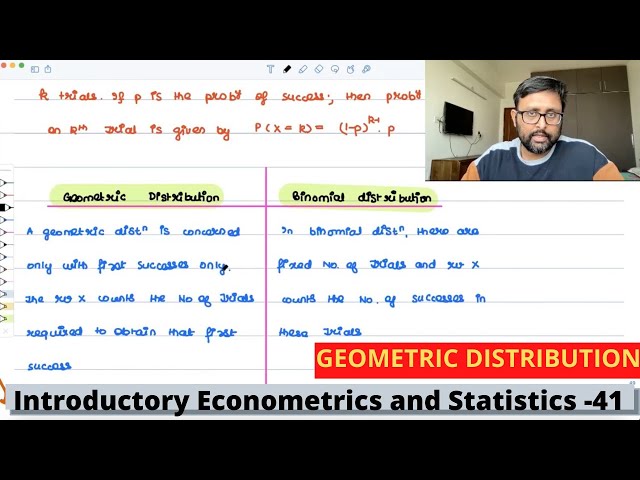
Geometric Distribution | Meaning | Example | 41 |
-

Poisson Distribution | Meaning | Examples |42 |
-

Normal Distribution | Meaning | Characteristics | Part 1 | 43 |
-

Normal Distribution | Simple Example | Part 2 | 44 |
-

Standard Normal Distribution | Meaning | Table | Example | Part 3 |
-

Student t-distribution | Meaning | Difference from Normal Distribution | 46 |
International Trade
-

International Trade | Law of Absolute Advantage | Meaning | Gains from Trade | 1 |
-
![[International Trade] Law of Comparative Advantage | Meaning | Gains from Trade | 2 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/m6rb7pmVZ-A/sddefault.jpg)
[International Trade] Law of Comparative Advantage | Meaning | Gains from Trade | 2 |
-
![[International Trade] Ricardian Model |Part 1| Production Possibility Frontier in Home & Foreign |3|](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Wvwdj2-Ai6Y/sddefault.jpg)
[International Trade] Ricardian Model |Part 1| Production Possibility Frontier in Home & Foreign |3|
-
![[International Trade] Ricardian Model | Part 2 | Autarky and Free Trade Equilibrium Price | 4 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Yv7SpinwhSA/sddefault.jpg)
[International Trade] Ricardian Model | Part 2 | Autarky and Free Trade Equilibrium Price | 4 |
-
![[International Trade] Ricardian Model | Part 3 |Relative Supply and Demand Curves in Autarky | 5 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/nc9jUprwOwQ/sddefault.jpg)
[International Trade] Ricardian Model | Part 3 |Relative Supply and Demand Curves in Autarky | 5 |
-
![[International Trade] Ricardian Model |Part 4 | World Relative Supply and Demand under Free Trade|6|](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ZafpTqgYW_E/sddefault.jpg)
[International Trade] Ricardian Model |Part 4 | World Relative Supply and Demand under Free Trade|6|
-
![[International Trade] Ricardian Model | Part 5 | Numerical Question | World Relative Supply | 7 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/LrOeX34sJbE/sddefault.jpg)
[International Trade] Ricardian Model | Part 5 | Numerical Question | World Relative Supply | 7 |
-
![International Trade [Ricardian Model]|Part 6| Numerical |Comparative Advantage| Gains from Trade|8|](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Z062d_pPQ-Y/sddefault.jpg)
International Trade [Ricardian Model]|Part 6| Numerical |Comparative Advantage| Gains from Trade|8|
-
![[International Trade] Ricardian Model | Part 7 | Relative Wages | 9 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/5IvOKRWmaDw/sddefault.jpg)
[International Trade] Ricardian Model | Part 7 | Relative Wages | 9 |
-
![[International Trade]Ricardian Model | Part 8 | Equilibrium Relative Prices |10|](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/BuE7UEE7GaQ/sddefault.jpg)
[International Trade]Ricardian Model | Part 8 | Equilibrium Relative Prices |10|
-
![[International Trade]Specific Factors Model | Part 1 | | Meaning | Assumptions | 11 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/RLv4pzu-GY8/sddefault.jpg)
[International Trade]Specific Factors Model | Part 1 | | Meaning | Assumptions | 11 |
-
![[International Trade] Specific Factors Model | Part 2 | Production Possibilities Frontier | 12 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/hWdiUX3e370/sddefault.jpg)
[International Trade] Specific Factors Model | Part 2 | Production Possibilities Frontier | 12 |
-
![[International Trade] Specific Factors Model | Part 3 | Prices, wages and Labour Allocation | 13 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/0Ac-JQBLXDs/sddefault.jpg)
[International Trade] Specific Factors Model | Part 3 | Prices, wages and Labour Allocation | 13 |
-

Specific Factors Model |Part 4 |Impact on Income Distribution due to change in Relative Prices |14|
-
![[International Trade]|Specific Factors Model | Part 5 | Trade in Specific Factors Model | 15 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/373m6nQfx3o/sddefault.jpg)
[International Trade]|Specific Factors Model | Part 5 | Trade in Specific Factors Model | 15 |
-
![[International Trade] Specific Factors Model | Part 6 | Income Distribution and Gains from Trade|16|](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/8NHflUa9QlM/sddefault.jpg)
[International Trade] Specific Factors Model | Part 6 | Income Distribution and Gains from Trade|16|
-
![[International Trade] Specific Factors Model | Part 7 | International labour Mobility | 17 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/jfFL3jWl-SU/sddefault.jpg)
[International Trade] Specific Factors Model | Part 7 | International labour Mobility | 17 |
-
![[International Trade] Heckscher Ohlin Model | Part 1 |Meaning &Comparison with Ricardian Model |18 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/X_8GCaxDSNo/sddefault.jpg)
[International Trade] Heckscher Ohlin Model | Part 1 |Meaning &Comparison with Ricardian Model |18 |
-

Stolper-Samuelson Theorem and Magnification Effect of Prices| Meaning and Intuition | H-O Model |19|
-
![[International Trade] Heckscher-Ohlin Model(Part 3) Meaning of Factor Price Equalisation Theorem|20|](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/lHg7UxANeZ8/sddefault.jpg)
[International Trade] Heckscher-Ohlin Model(Part 3) Meaning of Factor Price Equalisation Theorem|20|
-
![[International Trade] Heckscher-Ohlin Model | Part 4 | Assumptions of HO Theorem and Kinked PPC |21|](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/y8yjdFFxsHo/sddefault.jpg)
[International Trade] Heckscher-Ohlin Model | Part 4 | Assumptions of HO Theorem and Kinked PPC |21|
-

Heckscher-Ohlin Model | Part 5 | PPF | Isovalue line | Factor Intensity | Relative Abundance | 22 |
-

H-O Model | Part 6 | Relation between Input price & commodity price | Rybczynski Effect | 23 |
-
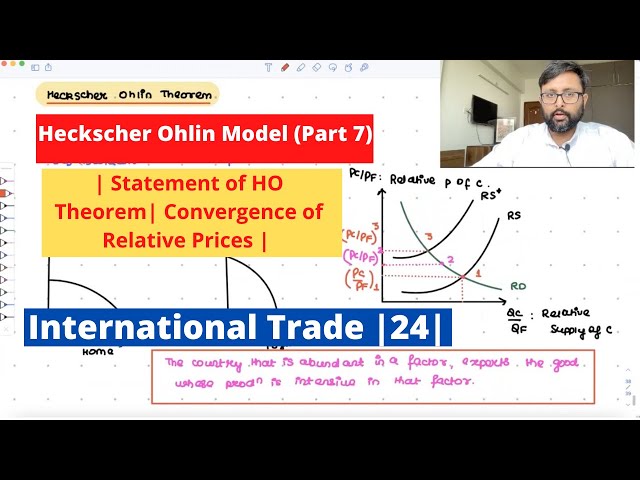
Heckscher Ohlin Model | Part 7 | Statement of H-O Theorem | Convergence of Relative Prices | 24 |
-
![[International Trade] HO Theorem | Part 8 | Meaning of Factor Price Equalisation Theorem | 25 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/HlfYq6ezylk/sddefault.jpg)
[International Trade] HO Theorem | Part 8 | Meaning of Factor Price Equalisation Theorem | 25 |
-
![[International Trade] H-O Theorem | Part 9 | Meaning of Rybczynski Theorem | 26 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Qw7PQnRMkvM/sddefault.jpg)
[International Trade] H-O Theorem | Part 9 | Meaning of Rybczynski Theorem | 26 |
-
![[International Trade] H-O Theorem (Part 10) | Leontief Paradox | Factor Intensity Reversal | 27 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/PCeCN9jxgI8/sddefault.jpg)
[International Trade] H-O Theorem (Part 10) | Leontief Paradox | Factor Intensity Reversal | 27 |
-
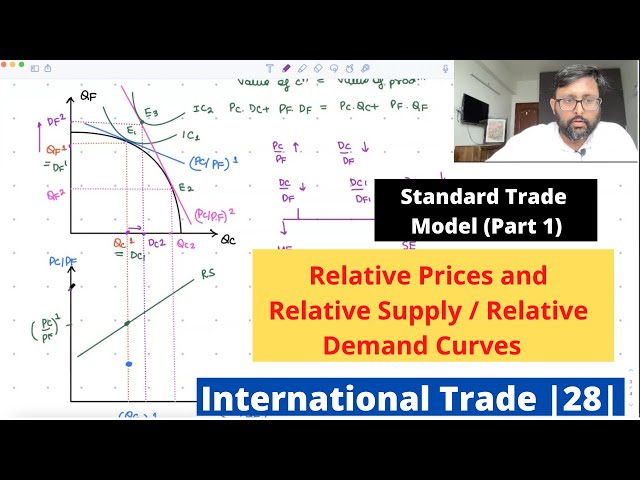
Standard Trade Model | Part 1 | Relative Price, Relative Supply, Relative Demand | 28 |
-

Standard Trade Model |Part 2|Terms of Trade |Strongly-Mildly Biased|Export-Import Biased Growth |29|
-
![International Trade | Standard Trade Model [Part 3] Immiserizing Growth | Meaning | 30 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Thni4HPGkno/sddefault.jpg)
International Trade | Standard Trade Model [Part 3] Immiserizing Growth | Meaning | 30 |
-

Standard Trade Model | Part 4 | Import Tariff | Export Subsidy | Terms of Trade | 31 |
-

Standard Trade Model | Part 5 | Implication of Terms of Trade due to Import Tariff | 32 |
-

Standard Trade Model | Part 6 | Implication of Terms of Trade Effects due to Export Subsidy | 33 |
-
![[International Trade] Instruments of Trade Policy | Import Quota | 34 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/x44y_r21y7k/sddefault.jpg)
[International Trade] Instruments of Trade Policy | Import Quota | 34 |
-
![[International Trade] External Economies of Scale | Sources | Market Equilibrium | 35 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/4DoUgxsrWNI/sddefault.jpg)
[International Trade] External Economies of Scale | Sources | Market Equilibrium | 35 |
-

External Economies of Scale | International Trade | Pattern of Trade | Historical Contingency | 36 |
-
![[International Trade]When Trade based on External economies is not necessarily welfare improving|37|](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/dvQBUua9P_g/sddefault.jpg)
[International Trade]When Trade based on External economies is not necessarily welfare improving|37|
-

External Economies of Scale |Dynamic Increasing Returns | Learning Curve | Infant Industry Arg |38|
-
![[International Trade] Internal Economies of Scale | Market Equilibrium | CC Curve | PP Curve | 39|](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/lVagxBCzeDs/sddefault.jpg)
[International Trade] Internal Economies of Scale | Market Equilibrium | CC Curve | PP Curve | 39|
-

Internal Economies of Scale | Trade in Monopolistic Competition | Increase in Market Size | 40 |
-

Internal Economies of Scale | Firm Responses to Trade | Trade affecting Industry Performance | 41 |
-

Internal Economies of Scale | Effects of Increase in Market Size| Gainers and Losers | 42 |
-

Internal Economies of Scale | Trade Costs and Export Decisions by Firms | 43 |
Basic Mathematics I
-
The Real number System | What are Real, rational, irrational, Integers,Whole,Natural numbers | 1 |
-
The Real Number Line | Meaning | 2 |
-

Properties of the Real Numbers | 3 |
-

Set Theory | Part 1 | What are sets how we denote them | Phi, Finite, Infinite Sets | 4 |
-

Set Theory | Part 2 | Set Operations | Union of Two sets Laws involving the Union of Sets | 5 |
-

Set Theory | Part 3 | Set Operations | Introduction to intersection and difference of Sets | 6 |
-

| Set Theory | Part 4 | Subsets and Powerset | 7 |
-
Set Theory | Part 5 | Introduction to Relations | 8 |
-

Set Theory | Part 6 | Reflexive and Anti Reflexive Relations | 9 |
-

Symmetric, Anti Symmetric and Asymmetric Relations on a set | 10 |
-

Transitive Relations | Examples of relations that are reflexive , symmetric, transitive | 11 |
-

Equivalence relation, Divisibility example | 12 |
-

Basic Modular Arithmetic and Equivalence classes | 13 |
-
Relations and Functions | Vertical Line Test | Basics | 14 |
-

Domain of a Function | 15 |
-

Functions | Part 3| Range of a function | Codomain and Range of a function | 16 |
-

Functions | Part 4 | Types of Functions | Injective, Bijective, Surjective and other types | 17 |
-
Functions | Part 5 | Types of Functions | Bijection and Inverse of a Function | 18 |
-

Functions | Part 6 | Types of Functions | Functions and Graphs | 19 |
-
Functions | Part 7 | Some important graphs | Cubic , Square Root, Modulus functions graphs | 20 |
-
Functions | Part 8 | Graph Transformation Vertical and Horizontal Shift |21|
-

Functions | Part 9 | Graph Transformation by Stretching and Reflection | 22 |
-
Functions | Part 10 | Inverse Function Basic to Graph |23|
-

Functions | Part 11 | How to use Graph to Find Area and to show that Inverse is Symmetric |24|
-

Functions | Part 12 | Even and Odd Functions |25|
-

Functions | Part 13 | The Absolute value Function Graph and Transformations |26|
-

Functions | Part 14 | Absolute Value Equations |27|
-
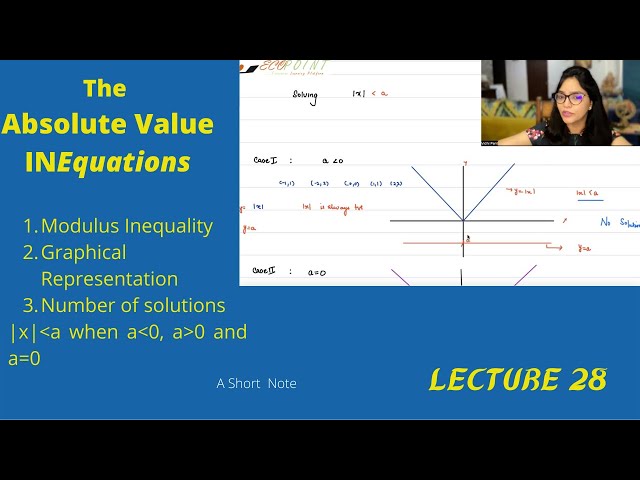
Functions | Part 15 | Absolute Value Inequations | 28 |
-
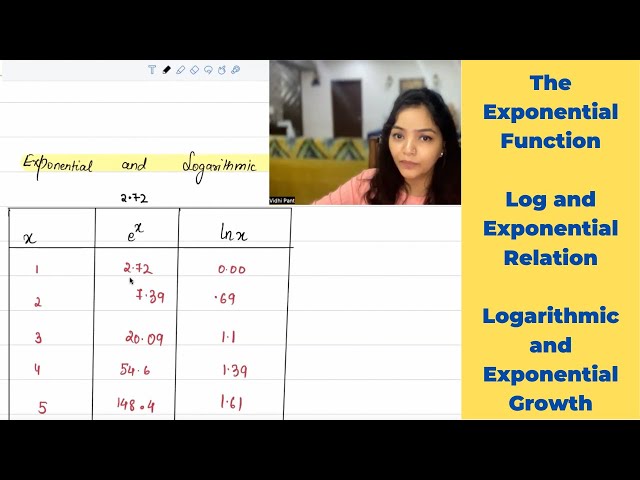
Functions | Part 16 | The Exponential Function | 29 |
Basic Mathematics II

Limits | Introduction to the Concept of Limits | An Intuitive Approach | 1 |

Limits | One Sided Limits | 2 |

Limits | Infinite Limits and Vertical Asymptotes | 3 |

Limits | limits at Infinity and Horizontal Asymptotes |4 |

Limits | Concept of Continuity |5|

Limits | Continuous Functions on Open and Closed Intervals | 6 |
Intermediate Macroeconomics
-

Solow Growth Model | Part 1 | Assumptions | Production function | 1 |
-

Solow Growth Model | Part 2 | Production function | Intensive form of Production function | 2 |
-

Solow Growth Model | Part 3 | Capital Accumulation Equation | 3 |
-

Solow Growth Model | Part 4 | Key Equation of Solow Model | 4 |
-

Solow Growth Model | Part 5 | Solow Diagram | Capital Deepening | Capital Widening | 5 |
-

Solow Growth Model | Part 6 | Comparative Statics |Derivation of steady state level of k and y | 6 |
-
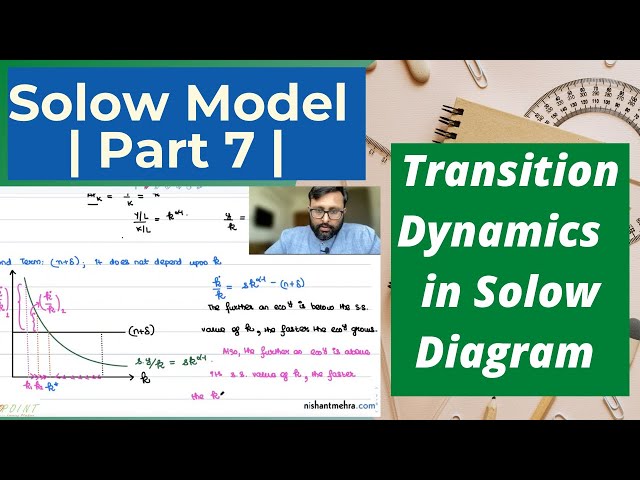
Solow Growth Model | Part 7 | Transition Dynamics in Solow Model | 7 |
-

Solow Growth Model with Technological Progress | Part 1 | 8 |
-

Solow Growth Model with Technological Progress | Part 2 | 9 |
-

Solow Growth Model with Technological Progress | Part 3 | Growth Effects | Level Effects | 10 |
-
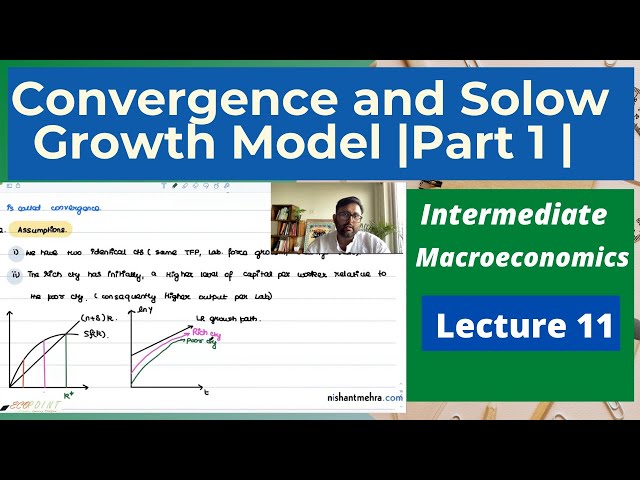
Convergence and Solow Growth Model | Part 1 | Meaning | 11 |
-
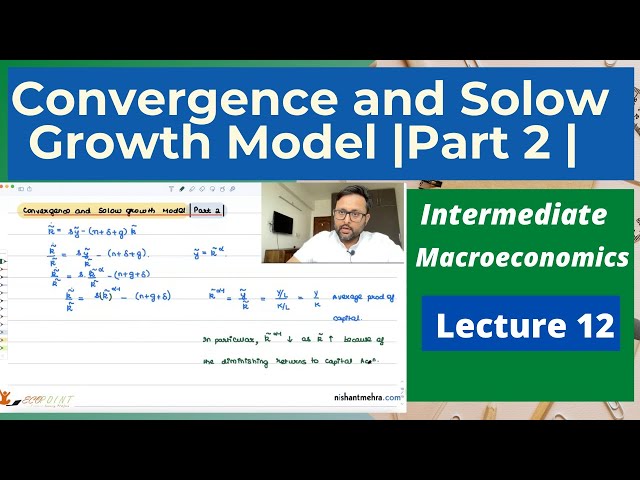
Convergence and Solow Growth Model | Part 2 | Diagram | Predictions| 12 |
-

Solow Growth Model | Complete | All Topics | 4 hours |
-

Economics of Ideas | Economics Growth | Intermediate Macroeconomics | Jones | 14 |
-

Economics of Ideas | Part 2 | Features of Ideas |Economics Growth | Intermediate Macroeconomics |15|
-

Uncertainty with Macroeconomic Models | Part 1 | Use of Monetary Policy and Fiscal Policy | 13 |
-

Uncertainty with Macroeconomic Models | Part 2 | Use of Monetary Policy and Fiscal Policy | 14 |
-

Uncertainty with Macroeconomic Models | Part 3 | Expectations and Policy| 15 |
-

Uncertainty with Macro Models |Part 4| Time Inconsistency | Rules better than discretion | 16 |
-

How Central banks can credibly commit to the announced policy | Part 5 | Uncertainty in Macro Models
-

Games Policy Makers play with Voters | Restraints on Policy Makers | Uncertainty of Macro Models|18|
-

Games between Policy Makers | Restraints on Policy Makers | Uncertainty of Macro Models |19|
-

Government Budget Constraint | Expression | Meaning | Fiscal Policy : Summing Up | 20 |
-

Government Budget Constraint | Full Repayment of Debt in Year 2 and Year t | 21 |
-

The Basic Logic of Ricardian Equivalence | Part 1 | 22 |
-

Economics of Ideas | Part 3 | Features of Ideas | Non Excludable & IRS | Intermediate Macro | 16 |
-

The Romer Model of Economic Growth | Romer Model of Endogenous Growth | Introduction | Part 1 | 17 |
-
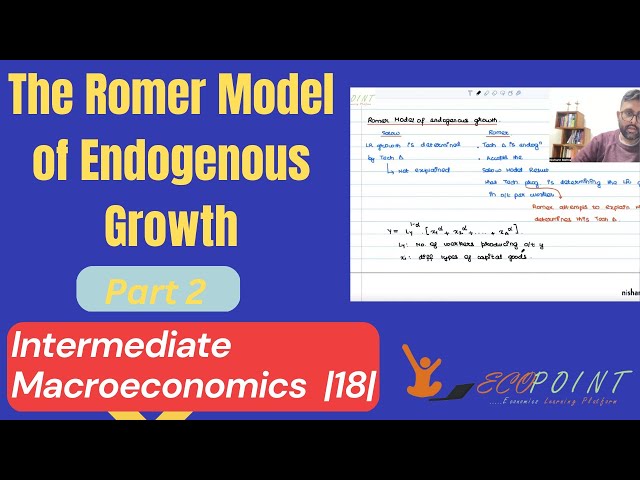
The Romer Model of Economic Growth | Part 2 | | Endogenous Technological Progress | 18 |
-
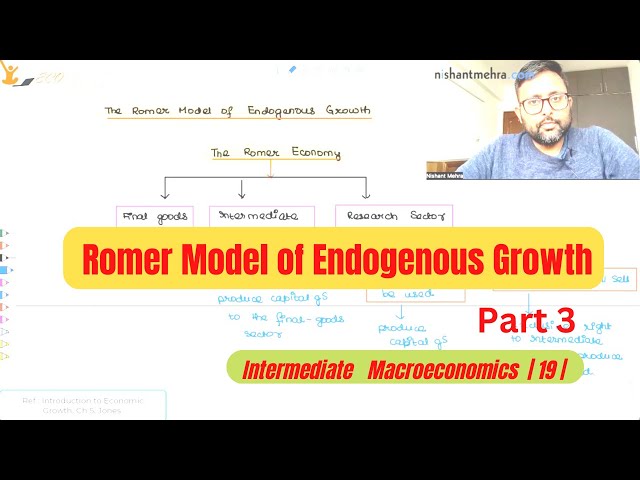
The Romer Model of Economic Growth | The Romer Economy | Part 3 |
-
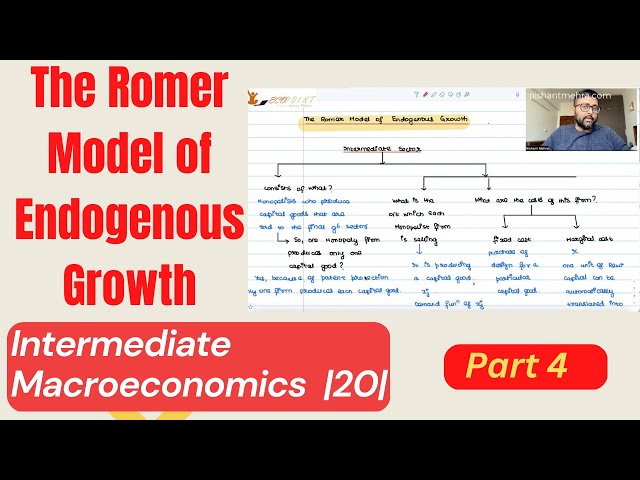
The Romer Model of Endogenous Growth | The Romer Economy | Intermediate Goods Sector | Part 4 |
-

The Romer Model | Endogenous Technological Progress | Part 5 |
-

The Romer Model | Endogenous Technological Progress | The Research Sector | Part 6 |
-
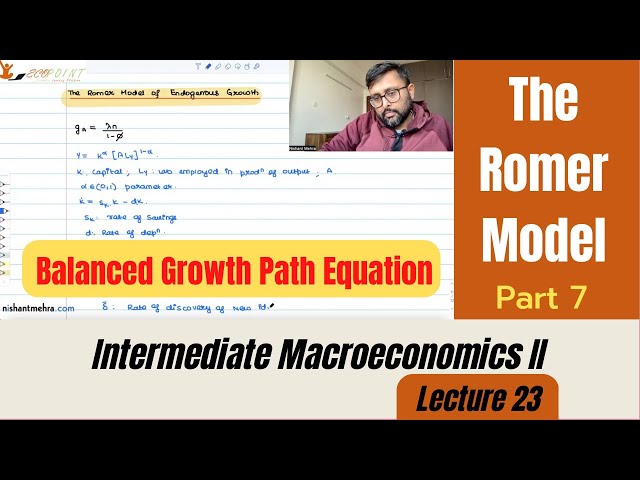
The Romer Model | Endogenous Technological Progress | Balanced Growth Path Equation| Part 7 |
-
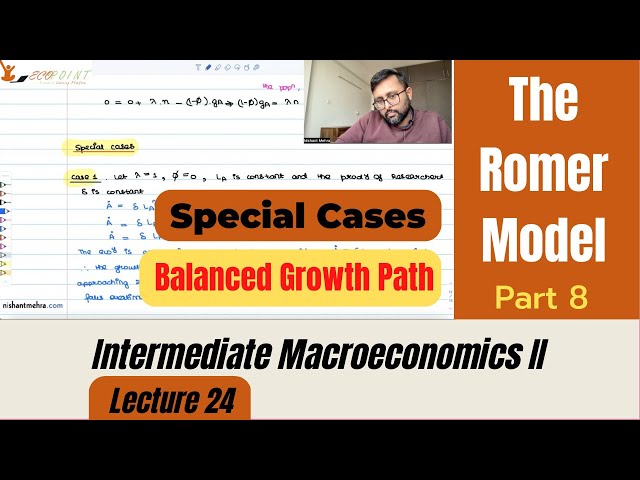
The Romer Model of Endogenous Growth| Endogenous Technological Progress | Special Cases | Part 8 |
-
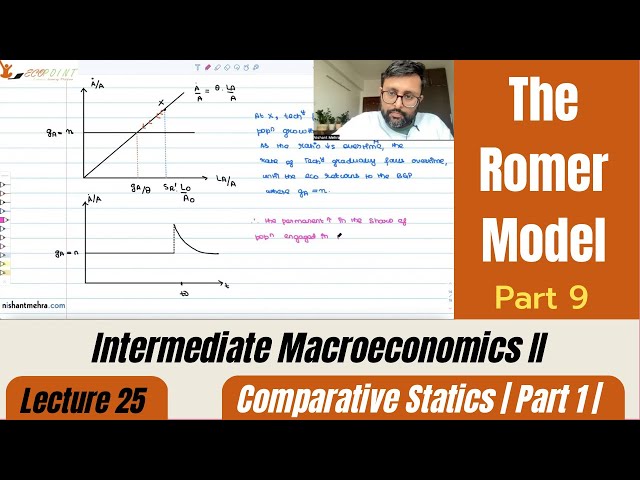
The Romer Model | Endogenous Technological Progress | Part 9 |
-

The Romer Model of Endogenous Growth | Romer Equation | IIT JAM Economics | UGC NET Economics |
-

Components of Balance of Payments | Introduction | Current Account and Capital Account | 26 |
-

External Accounts must Balance | Current Account +Capital Account = 0| Open economy Macroeconomics |
-

External Accounts must Balance | How current A/c surplus is used / current A/c deficit financed |28|
-

Summary of Economic Survey 2023 | IIT JAM Economics | UGC NET Economics |
-

Meaning of Real Exchange Rate | Real Exchange rate and Nominal Exchange Rate | RER formula | 29 |
-
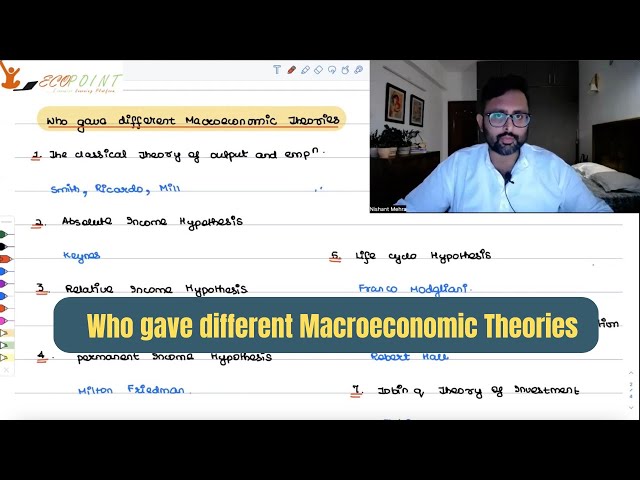
Who gave different theories in Macroeconomics| Names of different economists who propounded theories
-
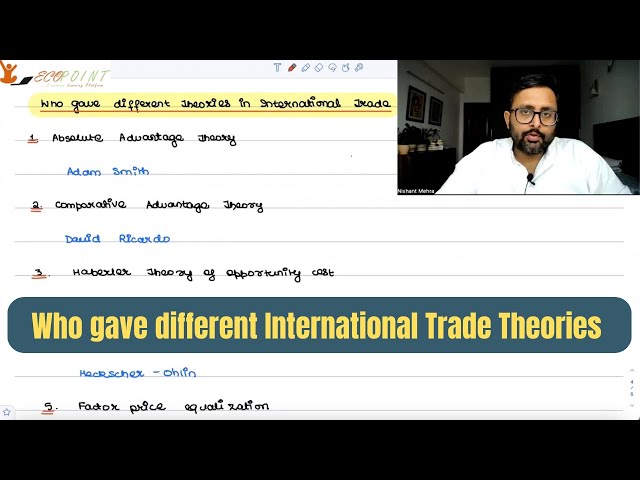
Who gave different theories in International Trade | Names of economists |
Pre-requisite for Intermediate Microeconomics I
-

Budget Constraint | Taxes , Rationing , Quantity Discounts | Very Basic | 1.1 |
-

Rules of Differentiation | With Economic Applications | Very Basic | 1.2 |
-

Maximization of One Variable Function | Profit function Example | Very Basic | 1.3 |
-

Partial Differentiation Introduction | Functions of Several Variables | Very Basic | 1.4 |
-
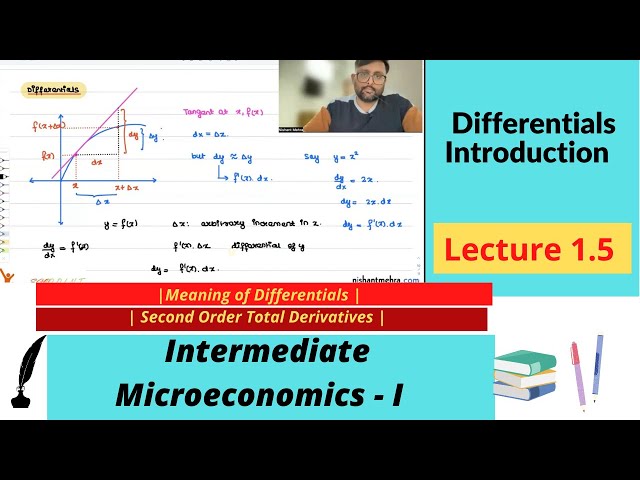
Differentials | Meaning | Total Derivatives | Second Order Derivative | 1.5 |
-

Necessary and Sufficient conditions |Maxima and Minima| Functions of several variables |Very Basic |
-
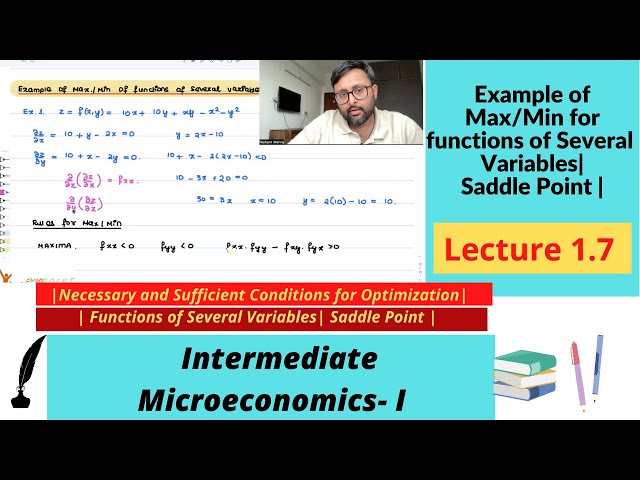
Example | Max or Min of functions of more than one variables | Saddle Point | Very Basic | 1.7 |
-

Lagrange Multiplier Method | Theory | Part 1 | Constrained Optimization | 1.8 |
-
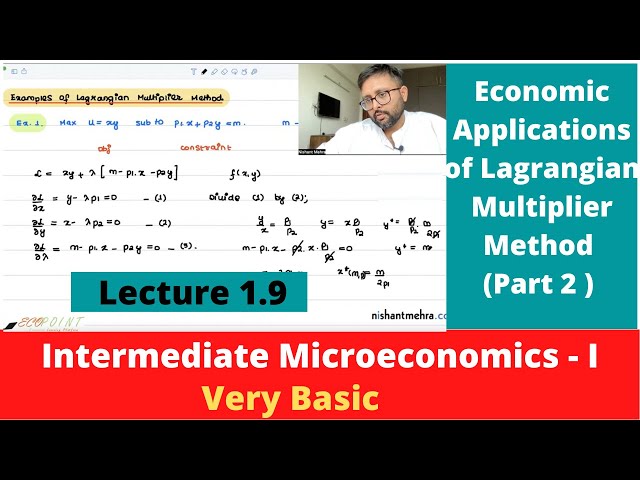
Lagrangian Multiplier Method | Examples | Simple Economic Applications | Part 2 | 1.9 |
-
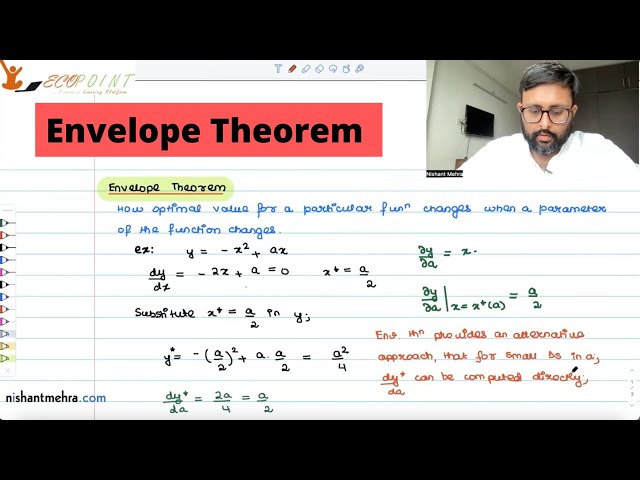
Envelope Theorem | Simple Examples | Meaning |
Basic Maths Revision
-

Basic Maths Revision | Part 1 | IGIDR | MSE (Madras School of Economics)
-

Basic Maths Revision | Part 2 | IGIDR | MSE (Madras School of Economics)
-
Basic Maths Revision | Part 3 | IGIDR | MSE (Madras School of Economics)
-

Basic Maths Revision | Part 4 | IGIDR | MSE (Madras School of Economics)
-

Basic Maths Revision | Part 5 | Probability Basics | IGIDR | Madras School of Economics | MSE |
Applied Econometrics
-

Applied Econometrics | Part 1 | Assumptions of CLRM in Matrix Notation | 1 |
-

Applied Econometrics | Part 2 | OLS estimator beta hat in Matrix Notation | 2 |
-

Applied Econometrics | Part 3 | Derivation of Variance Covariance Matrix beta hat | 3 |
-

Applied Econometrics | Part 4 | Some rules of Matrix Differentiation | beta hat in Matrix Notation |
Indian Economics
-

Mahalanobis Model | Economic Growth in Nehru Era | P Balakrishnan | Part 1 |
-

Wage Goods Model Vakil Brahmananda Plan | Economic Growth in Nehru Era | P Balakrishnan | Part 2 |
-

Critique of Wage Goods Model Vakil Brahmanand Plan | Part 3 | P Balakrishnan
-

Indian Economics MCQs | Part 1 | Economics Entrances | MSE | CUET |
-

Indian Economics MCQs | Part 2 | Economics Entrances | MSE | CUET |
-

Indian Economics MCQs | Part 3 | Economics Entrances | MSE | CUET |
-

Indian Economics | Comparison of growth rates in Nehru era | P Balakrishnan | Part 4 |
-

Misperceptions about Nehru Mahalanobis Model | Neglect of Agriculture | P Balakrishnan | Part 5 |
-

Misperceptions about Nehru Mahalanobis Model | Role of Public Sector | P Balakrishnan | Part 6 |
-

Indian Economics | India's Long Road | The Search for Prosperity | Vijay Joshi | Part 1 |
-

Indian Economics | India's Long Road | The Search for Prosperity | Vijay Joshi | Part 2 |
-

Indian Economics | India's Long Road | The Search for Prosperity | Vijay Joshi | Part 3 |
-

Indian Economics | Moving India to a New Growth Trajectory | Rakesh Mohan | Part 1 |
-

Indian Economics | Moving India to a New Growth Trajectory | Rakesh Mohan | Part 2 |
-

Indian Economics | Moving India to a New Growth Trajectory | Rakesh Mohan | Part 3 |
-

Indian Economics | Moving India to a New Growth Trajectory | Rakesh Mohan | Part 4 |
-

Indian Economics | India's Tryst with Destiny | Bhagwati and Panagariya | Part 1 |
-

Indian Economics | India's Tryst with Destiny | Bhagwati and Panagariya | Part 2 |
-

Indian Economics | Jean Dreze and Amartya Sen | India An Uncertain Glory | Part 1 |
-

Indian Economics | Dreze and Sen | India An Uncertain Glory | Part 2 |
-
Indian Economics | Dreze and Sen | India An Uncertain Glory | Part 3 |
-

Indian Economics | Dreze and Sen | India An Uncertain Glory | Part 4 | Development & Environment|18|
-

Indian Economics | Lecture 19 |Demographic Changes in India | Part 1 | KS James and Srinivas Goli |
-

Demographic Changes in India | Lecture 20 | KS James and Srinivas Goli | Part 2 | Mortality Decline
-

Demographic Changes in India | Lecture 21 | James and Srinivas Goli | Part 3 | Fertility Decline
-

Indian Economics | Lecture 22 | KS James and Srinivas Goli | Part 4 |Life Expectancy | Age Structure
-

Indian Economics | Lecture 23 | James and Goli | Part 5 | Preparedness for Demographic Change- I |
-

Indian Economics | Lecture 24 | James and Goli | Part 6 | Preparedness for Demographic Change II |
-

Indian Economics | Lecture 25 | Demographic Deposit, Dividend and Debt | Part 1| Sonalde Desai |
-

Indian Economics | Lecture 26 | Demographic Deposit, Dividend and Debt | Part 2 | Sonalde Desai |
-

Indian Economics | Lecture 27 | Demographic Deposit, Dividend and Debt | Part 3 | Sonalde Desai |
-

Indian Economics | Lecture 28 | Demographic Deposit, Dividend and Debt | Part 4 | Sonalde Desai |
-

Indian Economics | Lecture 29 | Triple Burden of Malnutrition | Part 1 | JV Meenakshi
-

Indian Economics | Lecture 30 | Triple Burden of Malnutrition | Part 2 | JV Meenakshi
-

Indian Economics | Lecture 31 | Triple Burden of Malnutrition | Part 3 | JV Meenakshi |
-

Indian Economics | Lecture 32 | Triple Burden of Malnutrition | Part 4 | JV Meenakshi
-

Indian Economics | Lecture 33 |Triple Burden of Malnutrition|Part 5 | JV Meenakshi | Energy Intake |
-

Indian Economics | Lecture 34 | Triple Burden of Malnutrition | Part 6 | JV Meenakshi |
-

Indian Economics | Lecture 35 | Triple Burden of Malnutrition | Part 7 | JV Meenakshi |
-

Indian Economics | Lecture 36 | Poverty Lines | Part 1 | Issues in Poverty Estimation |
-

Indian Economics | Lecture 37 | Inequality in India | Part 1 | Himanshu |
-

Indian Economics | Lecture 38 | Inequality in India | Part 2 | Himanshu |
-

Indian Economics | Lecture 39 | Inequality In India | Part 3 | Himanshu |
-

Indian Economics | Lecture 40 | Changes in Labour Market in India | Part 1 | Jayan Thomas |
-
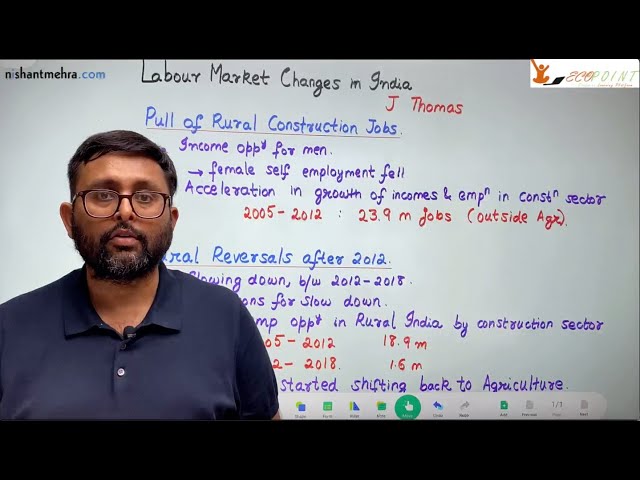
Indian Economics | Lecture 41 | Changes in Labour Market in India | Part 2 | Jayan Thomas |
-

Indian Economics | Lecture 42 | Changes in Labour Market in India | Jayan Thomas |
-

Indian Economics | India in Comparative Perspective | Part 1 | Dreaze and Sen |
-

Indian Economics | India in Comparative Perspective |Bangladesh Case Study|Part 2 | Dreze and Sen |
-

Indian Economics | India in Comparative Perspective | Part 3 |Comparison among BRIC| Dreze and Sen |
-

Indian Economics | Economic Reforms and Growth | India China | Part 1 | Pranab Bardhan | Lecture 46|
Indian Economics II
-

Indian Economics | India's Inward ReTurn | Shoumitro Chatterjee & Arvind Subramanian | Part 1|
-

India's Re Turn Inward | Arvind Subramanian | Shoumitro Chatterjee | Part 2 |
-

Rakesh Mohan and Partha Ray | Indian Financial Sector | Part 1 |
-

Indian Economics | Indian Financial Sector | Rakesh Mohan and Partha Ray | Part 2 | 4 |
-

Indian Economics | Indian Financial Sector | Rakesh Mohan and Partha Ray | Part 3 | 5 |
-

Indian Economics II | Trade Policy Reforms | Part 1 | Harsh Vardhan Singh |
-
Trade Policy Reforms | Part 2 | Harsh Vardhan Singh |
-

Summary of Economic Survey 2023 | Part 2 | IIT JAM Economics | UGC NET Economics |
-

Indian Economics | Trade Policy Reforms | Part 3 | Harsh Vardhan Singh | Tariff Reforms in India |8|
-

Indian Economics | Trade Policy Reforms | Part 4 | | Harsh Vardhan Singh | Lecture 9 |
-

Indian Economics | Trade Policy Reforms | Part 5 | | Harsh Vardhan Singh | Lecture 10 |
-

Trade Policy Reforms | Part 6 | | Harsh Vardhan Singh | Semester 6 | Indian economic services | 11 |
-

Trade Policy Reforms | Part 7 | | Harsh Vardhan Singh | Semester 6 | Indian economic services | 12 |
-

Employment Generation in Indian Manufacturing |UPSC Economics Optional |Indian economic services |
-

A Multitude of Labour Laws and their Reforms | Labour Laws Problems|Bhagwati and Panagariya| Part 2|
-

A Multitude of Labour Laws | Adverse Impact of Labour Laws | Bhagwati and Panagariya | Part 3 |
-

A Multitude of Labour Laws | Reforms required in Labour Laws | Bhagwati and Panagariya | Part 4 |
-
![[Indian Economics II] Transformation of Indian Agriculture | Mahendra Dev | Part 1 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/In6vPT0q-_A/sddefault.jpg)
[Indian Economics II] Transformation of Indian Agriculture | Mahendra Dev | Part 1 |
-
![[Indian Economics II] Transformation of Indian Agriculture | Mahendra Dev | Part 2 |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/vhRarZZo--8/sddefault.jpg)
[Indian Economics II] Transformation of Indian Agriculture | Mahendra Dev | Part 2 |
-

[Indian Economics II Transformation of Indian Agriculture | Part 3 | Mahendra Dev |
-
![[Indian Economics II] Transformation of Indian Agriculture | Part 4 | Mahendra Dev |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/0Cvs5fVhtjs/sddefault.jpg)
[Indian Economics II] Transformation of Indian Agriculture | Part 4 | Mahendra Dev |
-
![[Indian Economics II] Transformation of Indian Agriculture | Part 5 | Mahendra Dev |](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/tZA3xsXZRUY/sddefault.jpg)
[Indian Economics II] Transformation of Indian Agriculture | Part 5 | Mahendra Dev |
-
![[Indian Economy II] India's Services Sector | Rupa Chanda | Complete Reading](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/LidTo6Avui8/sddefault.jpg)
[Indian Economy II] India's Services Sector | Rupa Chanda | Complete Reading
Video Testimonials
-

Pranjal Das | ISI Kolkata, IIT JAM | Making Notes is helpful |
-
Aditi Thakur | ISI Delhi 2022 | MSQE | Consistency is the key |
-

Gautam Sodani | ISI MSQE 2022, Rank 4 | IIT JAM 2022, Rank 2 | Making Formula Book is beneficial |
-

Nayanika Nandi | Rank 8 | DSE 2022 | DSE Preparation Strategy |
-

Mahuri Salpekar | DSE 2022 | DSE Preparation Journey | Continuous Revision is important |
-

Gaurav | DSE 2022 | Rank 13 | DSE Preparation Strategy | B Tech, NMIMS |
-

Abhinav Soni | Rank 7 | DSE 2022 | DSE Preparation Strategy |
-

Kaustubh Rajput | Indian Economic Services | Rank 7 , IES 2022 | Preparation Strategy for IES exam |
-

Pragya Pratistha | Indian Economic Services Rank 15 | How to prepare for Indian Economic Services |
-

Priya Gupta | ISI 2023, Rank 21 | IIT Jam 2023, Rank 7 | Regular Revision is important |
-

Neelarka Roy | ISI 2023 | Rank 31 | Regular Revisions and doing different tests was helpful |
-
Ayan Chakraborty | ISI 2023, Rank 4 | IIT JAM 2023, Rank 4 | CUET PG Score 322 |
-

Mehak | Non Eco(H) | IGIDR, Rank 2 | JNU SSS, Rank 6 | CUET PG Economics, Score 272 |
-
Sagar Gala | Mumbai Uni. | CUET PG ECO. Score 301 | IIT JAM | IGIDR |
-

Nishchal Mittal | Indian Economic Services | Rank 1, IES 2023 | Preparation Strategy for IES exam |
-

Mihir Dev Choudhary | Rank 1 :CUET PG Economics Topper 2024 | Rank 1 : IIT JAM | Rank 3 : ISI MSQE |
-

Berninee Das | Rank 1: ISI MSQE | Rank 2 : IIT GATE Economics | CUET PG Economics (258 Marks) |
-

Mridhul K Iyer | ISI MSQE Rank 19 | IIT GATE Rank 5 | CUET PG Economics (240 marks)
-

Anushka Bansal | Rank 17 ISI MSQE | Rank 6 IIT GATE | Rank 13 IIT JAM | CUET PG Economics(260 Marks)
-

Ishika Aggarwal (Punjab University)|CUET PG Economics(248 Marks) | IIT GATE (Rank 46)|JNU (Rank 25)|
-

Reetika Gupta | Rank 4, IES 2024 | Indian Economic Services | Books , Syllabus and Preparation |
CUET PG Economics Entrance Daily Questions | MA Economics Entrance
-

AS curve from Cost function | CUET PG Economics 2023 | PGQP44 | Ques 1 | Perfect Competition |
-

Savings Rate in Solow Model | CUET PG Economics 2023 | CUET MA Economics Entrance | PGQP44 | 2 |
-

Basis and Dimensions | CUET PG Economics 2023 | CUET MA Economics Entrance | Ques 3 | PGQP44 |
-

Returns to Scale & Growth Accounting | CUET PG Economics 2023 | CUET MA Economics | PGPQ44 | Q4 |
-

Functions |Domain of logarithmic function |CUET PG Economics 2023 | CUET MA Economics |PGPQ44 | Q5 |
-

Mean, Median, Mode and Variance |CUET PG Economics 2023 | CUET MA Economics 2023 |PGPQ44 | Q6 |
-

One to one & Many to one functions | CUET PG Economics 2023 | CUET MA Economics 2023 |PGPQ44 | Q7 |
-

Indian Economics | Growth & Reforms |CUET PG Economics 2023 | CUET MA Economics 2023 |PGPQ44 | Q8 |
-

Subspace and Vector Space | CUET PG Economics 2023 | CUET MA Economics 2023 |PGPQ44 | Q9 |
-

Functional Equations | CUET PG Economics 2023 | CUET MA Economics 2023 |PGPQ44 | Q10 |
-

Statistics | Mean, Median, Mode |CUET PG Economics 2023 | CUET MA Economics 2023 |PGPQ44 | Q 11 |
-

Solow Residual & TFP | CUET PG Economics 2023 | CUET MA Economics 2023 | PGPQ44 | Q12|
-

Calculus limits |Exponential series | CUET PG Economics 2023 |CUET MA Economics 2023 |PGPQ44 | Q13 |
-

Integral Calculus | CUET MA Economics Entrance | CUET PG Economics Entrance 2023 | PGPQ44 | Q14 |
-
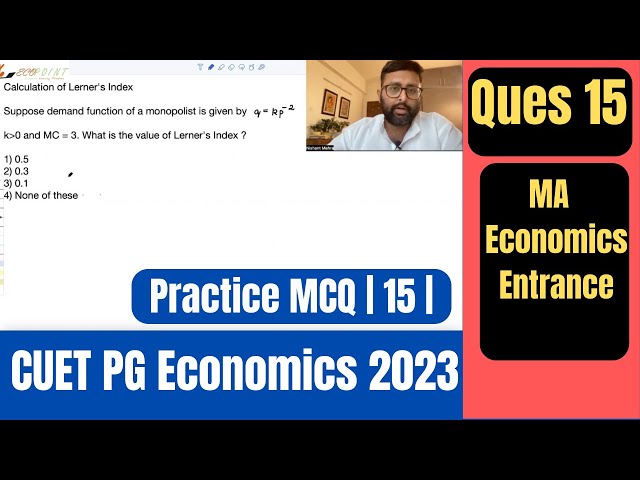
Lerner's Index | Monopoly |CUET MA Economics Entrance |CUET PG Economics Entrance 2023 |PGPQ44| Q15|
-

Homogenous function & Input- Output elasticity | CUET ME Economics Entrance 2023 | PGPQ44 | Q16 |
-

Matrices | Singular matrices | Properties of adjoint | CUET MA Economics Entrance 2023 |PGPQ44|Q17|
-

Monopoly | Perfect Price Discrimination| CUET PG Economics |CUET MA Economics Entrance | PGPQ44|Q18|
-

Closed & Open Economy Multiplier | CUET PG Economics |CUET MA Economics Entrance 2023 | PGPQ44 |Q19|
-

Properties of Matrices and Determinants|CUET MA Economics Entrance 2023|CUET PG Economics |PGPQ44 |
-

Probability Density functions |CUET MA Economics Entrance 2023|CUET PG Economics |PGPQ44 | Q21 |
-
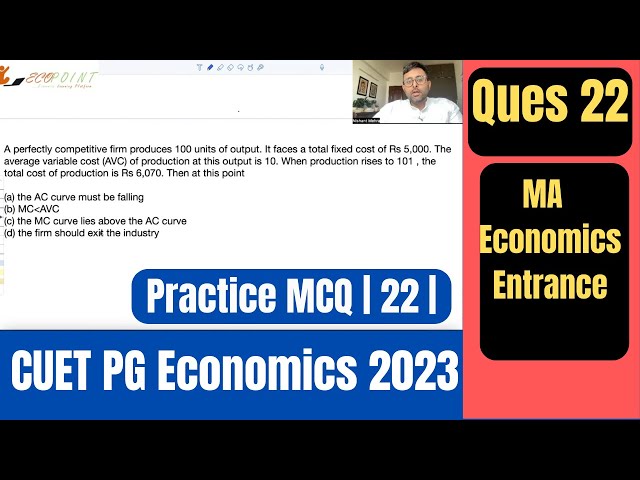
AC, AVC, MC |Cost Theory | CUET PG Economics 2023 | CUET MA Economics Entrance 2023 | PGPQ44 | Q22 |
-

Continuous Random Variables | Expected Value of X |CUET MA Economics Entrance 2023| PGPQ44 | Q23 |
-

Conditional probability|Bayes Thorem |CUET MA Economics Entrance 2023|CUET PG Economics|PGPQ44|Q24 |
-

Consumer Surplus | CUET PG Economics Entrance 2023 | CUET MA Economics Entrance 2023 | PGPQ44| Q25 |
-

Per Unit Subsidy | Fair Allocation |CUET PG Economics |CUET MA Economics Entrance 2023 | PGPQ44|Q26|
-

Mean, Median, Mode, Dispersion |CUET MA Economics Entrance 2023|CUET PG Economics|PGPQ44|Q27 |
-

Birthday Problem Permutation Combination | CUET MA Economics 2023|CUET PG Economics|PGPQ44|Q28 |
-

Balanced Budget & Simple Keynesian Model |CUET PG Economics 2023| CUET MA Economics 2023|PGPQ44|Q29|
-

Real GDP | Real Per Capita GDP | CUET PG Economics 2023 | CUET MA Economics 2023 | Q30 |
-

Set Theory Application| CUET PG Economics 2023 | CUET MA Economics 2023 | Q31 |
-

Inverse of an Exponential | Application | CUET PG Economics 2023 | CUET MA Economics 2023 | Q32 |
-

Finding limits and Derivatives | CUET PG Economics 2023 | CUET MA Economics 2023 | Q33 |
-

Adjoint of a Matrix | Eigenvalues | CUET PG Economics 2023 | CUET MA Economics 2023 | Q34 |
-
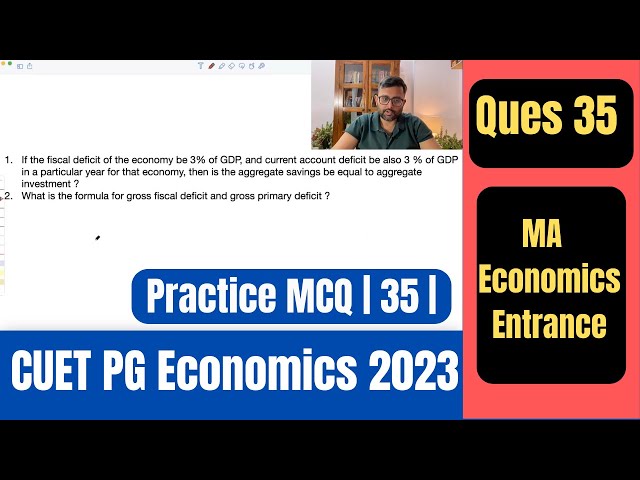
Gross fiscal deficit and primary deficit | CUET PG Economics 2023 | CUET MA Economics 2023 | Q35|
-

Maxima Minima | Liebnitz Theorem | CUET PG Economics 2023 | CUET MA Economics 2023 | Q36 |
-

Inflation rate , Expected Inflation | CUET PG Economics 2023 | CUET MA Economics Entrance | Q37|
-

Infinite Sum of a Series |Application of e^x | CUET PG Economics 2023 | CUET MA Economics 2023 |Q38|
-

Find the Number of local max min | CUET PG Economics 2023 | CUET MA Economics 2023 | Q39 |
-
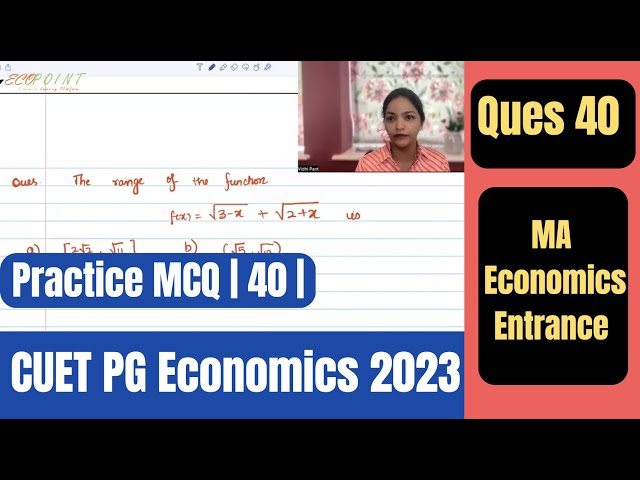
Range | Maxima Minima |Extreme Value Theorem | CUET PG Economics 2023 | CUET MA Economics 2023 |Q40|
-
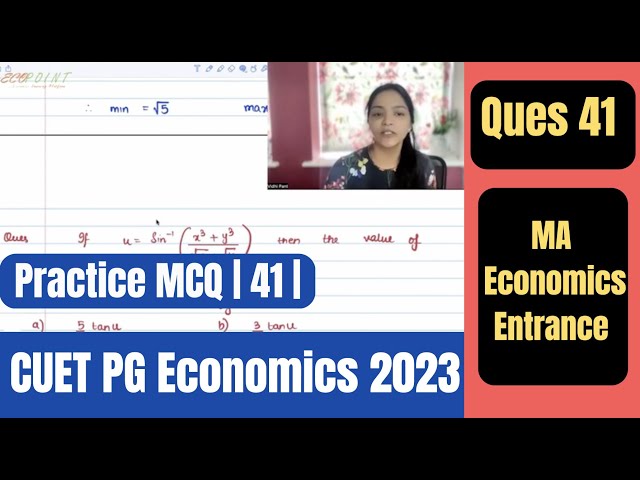
Eulers Theorem | Application of Derivatives | CUET PG Economics 2023 | CUET MA Economics 2023 | Q41|
-
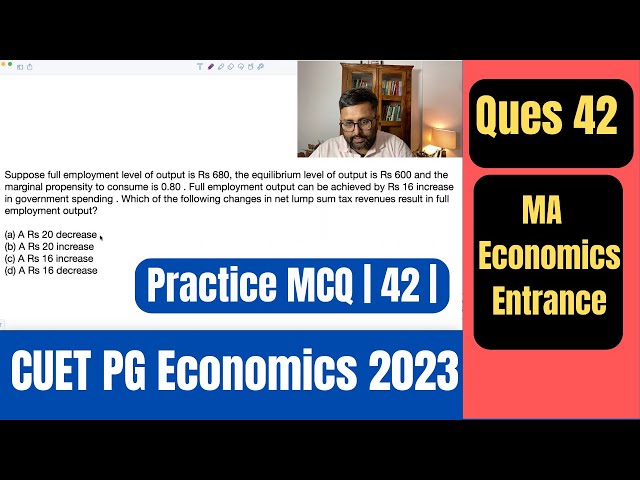
Tax Multiplier, Government Multiplier | CUET PG Economics Entrance | CUET MA Economics Entrance|Q42|
-

Probability | De Morgan's Law | Mean, Median | CUET PG Economics | CUET MA Economics Entrance| Q43 |
-

Expectedd value of a Continuous RV E(X^2) | CUET PG Economics | CUET MA Economics Entrance| Q43 |
-

Expectation of Poisson RV E(x+1) | CUET PG Economics Entrance | CUET MA Economics Entrance| Q45 |
-

Standard Normal | RV Probability and Inequalities |CUET PG Economics|CUET MA Economics Entrance|Q46|
-

Import Quota | International Trade | CUET PG Economics Entrance | CUET MA Economics Entrance |Q47|
-
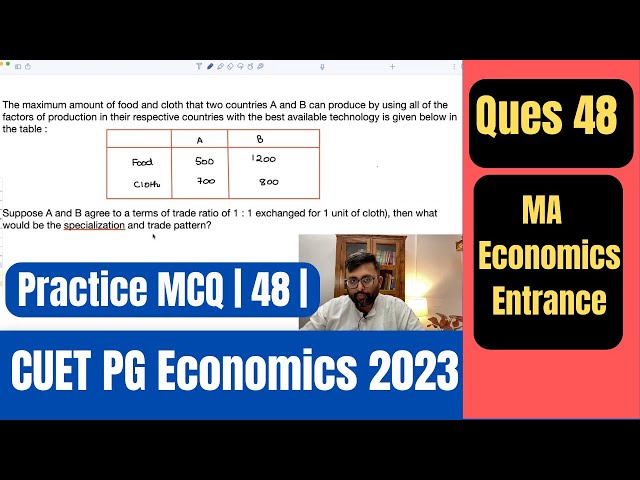
Comparative Advantage | International Trade | CUET MA Economics Entrance| CUET PG Economics |Q48|
-

Open Economy Macroeconomics| CUET PG Economics Entrance | CUET MA Economics Entrance 2023 |Q49|
-

Continuous,1to1, Increasing or Decreasing | CUET PG Economics | CUET MA Economics Entrance 2023|Q50|
